Elobixibat
- Molecular FormulaC36H45N3O7S2
- Average mass695.888 Da
AJG-533
AZD-7806


Elobixibat hydrate
Approved 2018/1/19 Japan pmda
TRADE NAME Goofice to EA Pharma
| エロビキシバット水和物 |
C36H45N3O7S2▪H2O : 713.9
[1633824-78-8] CAS OF HYDRATE

Gooffice ® tablet 5 mg (hereinafter referred to as Gooffice ® ) is an oral chronic constipation remedy drug containing as active ingredient Erobi vat having bile acid transporter inhibitory action. It is the world’s first bile acid transporter inhibitor.
Elobixibat is an inhibitor of the ileal bile acid transporter (IBAT),[1] undergoing development in clinical trials for the treatment of chronic constipation and irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C).
Mechanism of action
IBAT is the bile acid:sodium symporter responsible for the reuptake of bile acids in the ileum which is the initial step in the enterohepatic circulation. By inhibiting the uptake of bile acids, elobixibat increases the bile acid concentration in the gut, and this accelerates intestinal passage and softens the stool. Following several phase II studies, it is now undergoing phase III trials.[2]
Drug development
The drug was developed by Albireo AB, who licensed it to Ferring Pharmaceuticals for further development and marketing.[3] Albireo has partnered with Ajinomoto Pharmaceuticals, giving the Japan-based company the rights to further develop the drug and market it throughout Asia.[4]
- OriginatorAstraZeneca
- DeveloperAlbireo Pharma; EA Pharma
- Class2 ring heterocyclic compounds; Amides; Carboxylic acids; Laxatives; Small molecules; Sulfides; Sulfones; Thiazepines
- Mechanism of ActionSodium-bile acid cotransporter-inhibitors
- Orphan Drug StatusNo
- New Molecular EntityYes
Highest Development Phases
- RegisteredConstipation
- DiscontinuedDyslipidaemias; Irritable bowel syndrome
Most Recent Events
Approved 2018/1/19 japan pmda
- 24 Jan 2018Elobixibat is still in phase II trials for Constipation in Indonesia, South Korea, Taiwan, Thailand and Vietnam (Albireo pipeline, January 2018)
- 24 Jan 2018Discontinued – Phase-II for Irritable bowel syndrome in USA and Europe (PO) (Alberio pipeline, January 2018)
- 19 Jan 2018Registered for Constipation in Japan (PO) – First global approval
- In 2012, the compound was licensed to Ajinomoto (now EA Pharma) by Albireo for exclusive development and commercialization rights in several Asian countries. At the same year, the product was licensed to Ferring by Albireo worldwide, except Japan and a small number of Asian markets, for development and marketing. However, in 2015, this license between Ferring and Albireo was terminated and Albireo is seeking partner for in the U.S. and Europe. In 2016, Ajinomoto and Mochida signed an agreement on codevelopment and comarketing of the product in Japan.
Elobixibat
Elobixibat is an IBAT inhibitor approved in Japan for the treatment of chronic constipation, the first IBAT inhibitor to be approved anywhere in the world. EA Pharma Co., Ltd., a company formed via a 2016 combination of Eisai’s GI business with Ajinomoto Pharmaceuticals and focused on the gastrointestinal disease space, is the exclusive licensee of elobixibat for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders in Japan and other select countries in Asia (not including China) and is expected to co-market elobixibat in Japan with Mochida Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and to co-promote elobixibat in Japan with Eisai, under the trade name GOOFICE®.
We also believe that elobixibat has potential benefit in the treatment of NASH based on findings on relevant parameters in clinical trials of elobixibat that we previously conducted in patients with chronic constipation and in patients with elevated cholesterol and findings on other parameters relevant to NASH from nonclinical studies that we previously conducted with elobixibat or a different IBAT inhibitor. In particular, in a clinical trial in dyslipidemia patients, elobixibat given for four weeks reduced low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, with the occurrence of diarrhea being substantially the same as the placebo group. Also, in other clinical trials in constipated patients, elobixibat given at various doses and for various durations reduced LDL-cholesterol and, in one trial, increased levels of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Moreover, A4250 (an IBAT inhibitor) showed significant improvement (p < 0.05) on the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score in an established model of NASH in mice known as the STAM™ model and improvement in liver inflammation and fibrosis in another preclinical mouse model. We are considering conducting a Phase 2 clinical trial of elobixibat in NASH
These benzothiazepines possess ileal bile acid transport (IBAT) inhibitory activity and accordingly have value in the treatment of disease states associated with hyperlipidaemic conditions and they are useful in methods of treatment of a warm-blooded animal, such as man. The invention also relates to processes for the manufacture of said benzothiazepine derivatives, to pharmaceutical compositions containing them and to their use in the manufacture of medicaments to inhibit IBAT in a warm-blooded animal, such as man.
It is well-known that hyperlipidaemic conditions associated with elevated
concentrations of total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol are major risk factors for cardiovascular atherosclerotic disease (for instance “Coronary Heart Disease: Reducing the Risk; a Worldwide View” Assman G., Carmena R. Cullen P. et al; Circulation 1999, 100, 1930-1938 and “Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease: A Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association” Grundy S, Benjamin I., Burke G., et al; Circulation, 1999, 100, 1134-46). Interfering with the circulation of bile acids within the lumen of the intestinal tracts is found to reduce the level of cholesterol. Previous established therapies to reduce the concentration of cholesterol involve, for instance, treatment with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, preferably statins such as simvastatin and fluvastatin, or treatment with bile acid binders, such as resins. Frequently used bile acid binders are for instance cholestyramine and cholestipol. One recently proposed therapy (“Bile Acids and Lipoprotein Metabolism: a Renaissance for Bile Acids in the Post Statin Era” Angelin B, Eriksson M, Rudling M; Current Opinion on Lipidology, 1999, 10, 269-74) involved the treatment with substances with an IBAT inhibitory effect.
Re-absorption of bile acid from the gastro-intestinal tract is a normal physiological process which mainly takes place in the ileum by the IBAT mechanism. Inhibitors of EBAT can be used in the treatment of hypercholesterolaemia (see for instance “Interaction of bile acids and cholesterol with nonsystemic agents having hypocholesterolaemic properties”, Biochemica et Biophysica Acta, 1210 (1994) 255- 287). Thus, suitable compounds having such inhibitory IBAT activity are also useful in the treatment of hyperlipidaemic conditions.
Compounds possessing such IBAT inhibitory activity have been described, see for instance the compounds described in WO 93/16055, WO 94/18183, WO 94/18184, WO 96/05188, WO 96/08484, WO 96/16051, WO 97/33882, WO 98/38182, WO 99/35135, WO 98/40375, WO 99/35153, WO 99/64409, WO 99/64410, WO 00/01687, WO 00/47568, WO 00/61568, WO 01/68906, DE 19825804, WO 00/38725, WO 00/38726, WO 00/38727, WO 00/38728, WO 00/38729, WO 01/68906, WO 01/66533, WO 02/50051 and EP 0 864 582.
A further aspect of this invention relates to the use of the compounds of the invention in the treatment of dyslipidemic conditions and disorders such as hyperlipidaemia, hypertrigliceridemia, hyperbetalipoproteinemia (high LDL), hyperprebetalipoproteinemia (high VLDL), hyperchylomicronemia, hypolipoproteinemia, hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipoproteinemia and hypoalphalipoproteinemia (low HDL). In addition, these compounds are expected to be useful for the prevention and treatment of different clinical conditions such as atherosclerosis, arteriosclerosis, arrhythmia, hyper-thrombotic conditions, vascular dysfunction, endothelial dysfunction, heart failure, coronary heart diseases, cardiovascular diseases, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, peripheral vascular diseases, inflammation of cardiovascular tissues such as heart, valves, vasculature, arteries and veins, aneurisms, stenosis, restenosis, vascular plaques, vascular fatty streaks, leukocytes, monocytes and/or macrophage infiltration, intimal thickening, medial thinning, infectious and surgical trauma and vascular thrombosis, stroke and transient ischaemic attacks.
PATENTS
WO 2002050051
| STARKE, Ingemar; (SE). DAHLSTROM, Mikael; (SE). BLOMBERG, David; (SE) |
ASTRAZENECA
SYNTHESIS
WO 2002050051, WO 1996016051
PATENT
WO 2003051821
WO 2003020710
TW I291951
WO 2013063512
WO 2013063526
US 20140323412
EP 3012252
PATENT
https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2003020710A1/und
PATENT
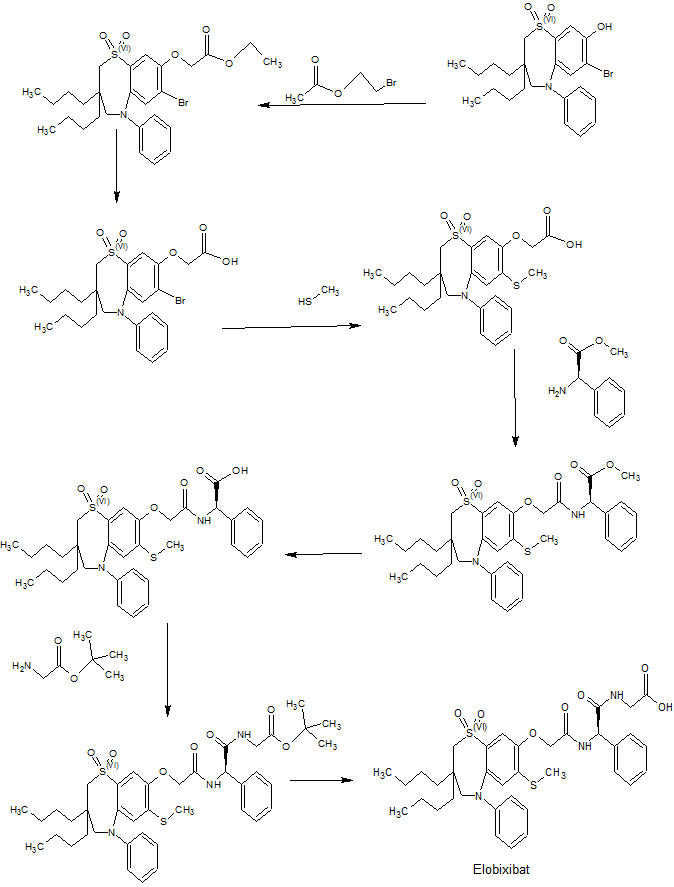
WO 02/50051 discloses the compound 1 ,1 -dioxo-3,3-dibutyl-5-phenyl-7-methylthio-8-(/V-{(R)-1 ‘-phenyl-1 ‘- [/V-(carboxymethyl)carbamoyl]methyl}carbamoylmethoxy)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1 ,5-benzothiazepine (elobixibat; lUPAC name: /V-{(2R)-2-[({[3,3-dibutyl-7-(methylthio)-1 ,1 -dioxido-5-phenyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1 ,5-benzothiazepin-8-yl]oxy}acetyl)amino]-2-phenyl-ethanolyl}glycine). This compound is an ileal bile acid transporter (I BAT) inhibitor, which can be used in the treatment or prevention of diseases such as dyslipidemia, constipation, diabetes and liver diseases. According to the experimental section of WO 02/50051 , the last synthetic step in the preparation of elobixibat consists of the hydrolysis of a ie f-butoxyl ester under acidic conditions. The crude compound was obtained by evaporation of the reaction mixture under reduced pressure and purification of the residue by preparative HPLC using acetonitrile/ammonium acetate buffer (50:50) as eluent (Example 43). After freeze drying the product, no crystalline material was identified.
Example 1
Preparation of crystal modification I
Toluene (1 1 .78 L) was charged to a 20 L round-bottom flask with stirring and 1 ,1 -dioxo-3,3-dibutyl-5-phenyl-7-methylthio-8-(/V-{(R)-1 ‘-phenyl-1 ‘-[/\/’-(i-butoxycarbonylmethyl)carbamoyl]-methyl}carbamoylmethoxy)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1 ,5-benzothiazepine (2.94 kg) was added. Formic acid (4.42 L) was added to the reaction mass at 25-30 °C. The temperature was raised to 1 15-120 °C and stirred for 6 hours. The reaction was monitored by HPLC to assure that not more than 1 % of the starting material remained in the reaction mass. The reaction mass was cooled to 40-43 °C. Purified water (1 1 .78 L) was added while stirring. The reaction mass was further cooled to 25-30 °C and stirred for 15 min.
The layers were separated and the organic layer was filtered through a celite bed (0.5 kg in 3 L of toluene) and the filtrate was collected. The celite bed was washed with toluene (5.9 L), the filtrates were combined and concentrated at 38-40 °C under vacuum. The reaction mass was then cooled to 25-30 °C to obtain a solid.
Ethanol (3.7 L) was charged to a clean round-bottom flask with stirring, and the solid obtained in the previous step was added. The reaction mass was heated to 40-43 °C and stirred at this temperature for 30 min. The reaction mass was then cooled to 25-30 °C over a period of 30 min., and then further cooled to 3-5 °C over a period of 2 h, followed by stirring at this temperature for 14 h. Ethanol (3.7 L) was charged to the reaction mass with stirring, while maintaining the temperature at 0-5 °C, and the reaction mass was then stirred at this temperature for 1 h. The material was then filtered and washed with ethanol (1 .47 L), and vacuum dried for 30 min. The material was dried in a vacuum tray dryer at 37-40 °C for 24 h under nitrogen atmosphere. The material was put in clean double LDPE bags under nitrogen atmosphere and stored in a clean HDPE drum. Yield 1 .56 kg.
Crystal modification I has an XRPD pattern, obtained with CuKal -radiation, with
characteristic peaks at °2Θ positions: 3,1 ± 0.2, 4,4 ± 0.2, 4,9 ± 0.2, 5,2 ± 0.2, 6,0 ± 0.2, 7,4 ± 0.2, 7,6 ± 0.2, 7,8 ± 0.2, 8,2 ± 0.2, 10,0 ± 0.2, 10,5 ± 0.2, 1 1 ,3 ± 0.2, 12,4 ± 0.2, 13,3 ± 0.2, 13,5 ± 0.2, 14,6 ± 0.2, 14,9 ± 0.2, 16,0 ± 0.2, 16,6 ± 0.2, 16,9 ± 0.2, 17,2 ± 0.2, 17,7 ± 0.2, 18,0 ± 0.2, 18,3 ± 0.2, 18,8 ± 0.2, 19,2 ± 0.2, 19,4 ± 0.2, 20,1 ± 0.2, 20,4 ± 0.2, 20,7 ± 0.2, 20,9 ± 0.2, 21 ,1 ± 0.2, 21 ,4 ± 0.2, 21 ,8 ± 0.2, 22,0 ± 0.2, 22,3 ± 0.2, 22,9 ± 0.2, 23,4 ± 0.2, 24,0 ± 0.2, 24,5 ± 0.2, 24,8 ± 0.2, 26,4 ± 0.2,‘27,1 ± 0.2 and 27,8 ± 0.2. The X-ray powder diffractogram is shown in FIG. 4.
PATENT
WO 2014174066
| エロビキシバット水和物 Elobixibat Hydrate  C36H45N3O7S2▪H2O : 713.9 [1633824-78-8] |
References
- Jump up^ “INN for A3309 is ELOBIXIBAT”. AlbireoPharma. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 5 December 2012.
- Jump up^ Acosta A, Camilleri M (2014). “Elobixibat and its potential role in chronic idiopathic constipation”. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 7 (4): 167–75. doi:10.1177/1756283X14528269. PMC 4107709
![Freely accessible Freely accessible]() . PMID 25057297.
. PMID 25057297. - Jump up^ Grogan, Kevin. “Ferring acquires rights to Albireo’s bowel drug”. PharmaTimes. Retrieved 23 March 2017.
- Jump up^ “Ajinomoto Pharmaceuticals and Albireo Announce Japan and Asia License Agreement for Elobixibat”. Albireo. Retrieved 5 December2012.[permanent dead link]
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C36H45N3O7S2 |
| Molar mass | 695.89 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
//////////Elobixibat hydrate, japan 2018, A-3309, AJG-533, Goofice, A 3309, AJG 533, AZD 7806
CCCCC1(CN(C2=CC(=C(C=C2S(=O)(=O)C1)OCC(=O)NC(C3=CC=CC=C3)C(=O)NCC(=O)O)SC)C4=CC=CC=C4)CCCC























































 +91- 999-997-2051
+91- 999-997-2051 info@synthesiswithcatalysts.com
info@synthesiswithcatalysts.com





























 DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..
DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..


 amcrasto@gmail.com
amcrasto@gmail.com